by Potnuru Hatakesh
Adoption of "The Cloud" is growing significantly as more a enterprises start to see and experiencing the value in agility, scalability, and cost savings.
As cloud platforms grow in popularity, businesses are focusing on developing methods to integrate data from traditional enterprise systems to cloud-based systems. Data integration will always be a challenge because of the need to clearly understand the nature of each system, technology behaviors, available communication channels, data exchange formats, and many other applicable elements.
Cloud data integration tools are emerging to help accomplish the integration of data from within cloud environments and among different cloud data sources.
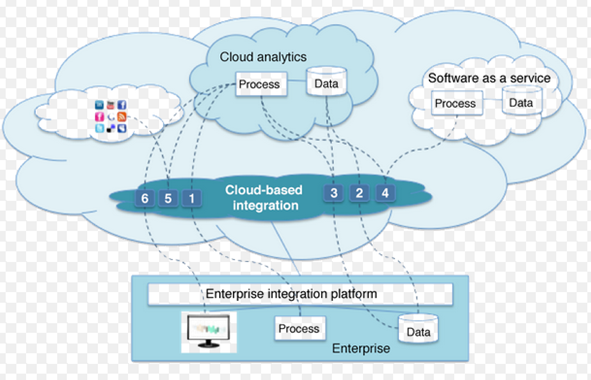
Features & Benefits of Cloud-Based Data Integration
- Public and Private Cloud options available.
- Provides pre built connectors to Cloud and On-Premise Apps and Services.
- Provides ability to build and extend analytical applications.
- Provides connectors to Salesforce.com and other cloud applications.
- Provides connectors to cloud databases such as Hadoop, Hive etc.
- Provides the capability for large volume data movement to achieve cloud application integration.
- Provides scalability by enabling additional nodes.
Popular Cloud-Based Data Integration Tools
- Informatica Cloud
- SnapLogic Elastic Integration Platform
- Attunity
- Microsoft Azure BizTalk Services
Informatica Cloud Architecture
In Informatica Cloud, metadata and components of Informatica Powercenter are moved to the cloud. Some data adapters were added. The actual data integration still takes place on-premise.
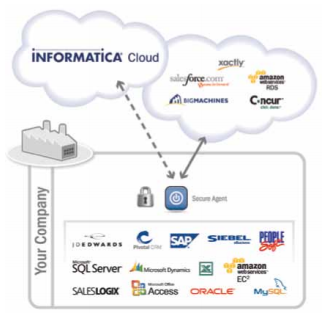
(Source: Informatica Cloud userguide)
Informatica’s Cloud secure agent connects directly from source to the target systems. A customer's data is never staged or stored on Informatica Cloud. The operations manager provides both line-of-business and IT departments with secure access to integration jobs.
SnapLogic Elastic Integration Platform Architecture
A Snaplex is the data processing component of the SnapLogic Integration Cloud. Customers can deploy one or many Snaplexes to run pipelines and process data. Snaplexes come in two flavors:
- On-premise Snaplex (also known as “Groundplex”)
- Cloud Snaplex (also known as “Cloudplex”)
The SnapLogic Integration Cloud is architected with the concept of software-defined networking (SDN). The system is decoupled into two main areas: a control plane and a data plane.
Control Plane
The control plane controls where and how data is processed based on user configuration & preferences and some optimization algorithms.
Data Plane
The data plane performs the actual processing of data based on the instructions provided by the control plane.
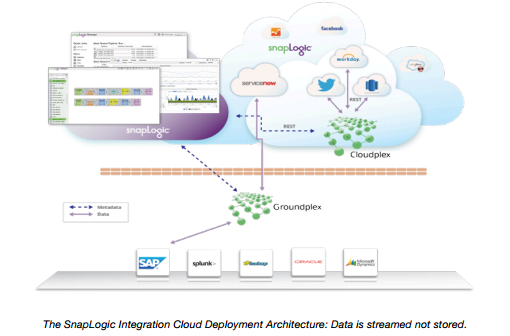
The Snaplex can elastically expand and contract based on data traffic flowing through it. The unit of scalability inside Snaplex is a Java virtual machine (JVM), referred to as a “Node”. The control plane has built-in “smarts” to automatically scale the Snaplex, in order to handle variable traffic loads. With this elastic integration, it can handle data at any volume, variety and velocity, without having to do rigorous complex and costly capacity planning and provisioning.
Summary
When building a data warehouse for data coming from different cloud sources, it is considered a best practice to clearly understand and define the structure of the data. This preparation allows for the analysis of the integration options available to integrate those specific data structures. This type of plainning on the front-end helps avoid the maintenance challenges that can arise from data structures, change data capture, and data loading at a later stages when actions become more costly.
 |
Potnuru Hatakesh is a Lead Consultant at KPI Partners. He specializes in data warehousing, cloud applications, and business intelligence. Check out Potnuru's blog at KPIPartners.com. |



